Consequences of the new DIN 4109 “Sound insulation in buildings”
The new German standard DIN 4109 “Sound insulation in buildings” is supposed to replace the old version of DIN 4109 from 1989 in the last quarter of this year. The revision of the standard had taken more than ten years; at the end of the process there is a standard, which, in respect of the calculation method, primarily follows the European series of standards DIN EN12354. By the legal introduction of DIN 4109, the verification of sound insulation becomes more complex and is hardly possible without the respective software program. In return, the results more precisely indicate the sound insulation to be expected, which, apart from that, in terms of multi-story residential construction is only marginally tightened by the new standard.
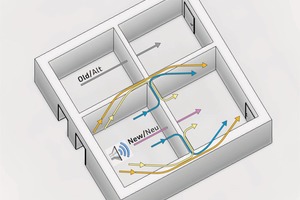
While, so far, the tables of the supplementary sheet 1 of DIN 4109 provided many values, which the user could interpolate, a lot of parameters will have to be taken into consideration in future, in order to determine 12 additional sound transmission paths via the joints with the four flanking components (Fig. 1), aside from the direct sound transmission path through the separating element, for finally calculating the horizontal and vertical airborne sound transmission paths R‘w. It is new that, apart from the mass of the component under consideration, further relevant parameters, such as coupling length, surface areas of flanking components or types of connection, are used for the calculation.
Impact sound transmission values L’n,w
It is less complicated to determine the horizontal and vertical impact sound transmission values in solid construction. Apart from the floor construction made of floating screed, impact sound insulation and apartment separating floor as well as possible suspended ceilings, the mass of the flanking walls and potential facing walls have an influence on the impact sound transmission value L’n,w.
The maximum permitted values concerning the horizontal and vertical impact sound transmission values L’n,w have been reduced from 53 dB to 50 dB in the field of multi-story residential construction. This means that the standard becomes more stringent in multi-story residential construction. The limit values R’w for airborne sound transmission through apartment separating walls and apartment separating floors at 53 dB and 54 dB remain otherwise unchanged compared to DIN 4109, and even the recommendations for an increased sound insulation were not included.
Sound calculation software of DW Systembau
Supported by MFPA Leipzig – Gesellschaft für Materialforschung und Prüfungsanstalt für das Bauwesen Leipzig mbH (Leipzig Materials Research and Testing Institute), DW Systembau has developed a program on the basis of E DIN 4109 for the preliminary design of horizontal and vertical sound transmissions especially for multi-story residential construction. At a very early stage, the program allows clients, architects and planners to check the level of sound insulation that can be achieved by the selected wall and floor construction and/or what kind of adjustments are worthwhile to be made, in order to obtain the target sound insulation values.
The program is available on the internet at //www.dw-systembau.de" target="_blank" >www.dw-systembau.de:www.dw-systembau.de to any interested user.
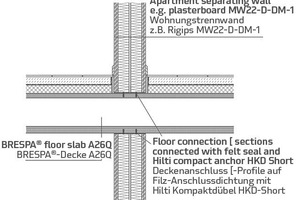
At the same time, DW Systembau assigned MFPA Leipzig to perform longitudinal sound measurements on solid precast prestressed concrete floor slabs and on precast prestressed concrete hollow core floor slabs, and to determine specific values for the joint insulation, in order to estimate the influence of the cavities on the sound transmission through apartment separating walls made of non-bearing lightweight walls. The outcome reveals that solid floor slabs, in comparison to precast prestressed concrete floor slabs, featuring equal thicknesses, achieve better values because of their increased mass, but that Brespa floor slabs achieved significantly higher joint insulation values than specified by E DIN 4109. These values have been incorporated in the new preliminary design program.
Moreover, the results of the measurements do not provide any evidence to doubt the calculation method of the new DIN 4109, which does not differentiate between solid floor slabs and hollow core floor slabs of the same weight.
Floor systems and
sound insulation
If the slab geometries of precast prestressed concrete floor slabs do not have a negative impact on the sound insulation, then what are the influences of precast prestressed concrete floor slabs of the lower weights on sound insulation in residential construction? This question was pursued with the collaboration of MPFA Leipzig taking the longitudinal sound measurements and the new calculation method of E DIN 4109 into consideration, investigating each of the four longitudinal sound transmission paths.
Generally, concrete floor slabs used as upper and lower flanking element with their high self-weight have excellent sound insulation values concerning the horizontal airborne sound transmission values R‘w. In this regard, it is of secondary importance whether solid floor slabs or precast prestressed concrete hollow core floor slabs are installed, because noticeable improvements through higher floor weights are hardly possible at all. This is different in case of apartment separating walls. Their weight has significant influence on the horizontal sound insulation. Hence, the requirements of DIN 4109 and in particular the enhanced requirements according to supplementary sheet 2 of DIN 4109 can be achieved in multi-story residential construction only by means of heavy apartment separating walls made of sand-lime blocks or reinforced concrete and/or by means of lightweight double-leaf construction or facing layers.
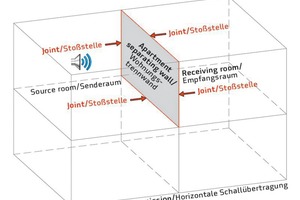
Vertical airborne sound transmission values R’w
The vertical airborne sound transmission is due to apartment separating floors and flanking walls. This individual case – as the calculation results provided by the sound software show – is normally more favorable in terms of sound insulation than the horizontal sound transmission R’w, so that the general rule is: If the requirements on the horizontal airborne sound are met, then this is also true for the requirements of the vertical airborne sound.
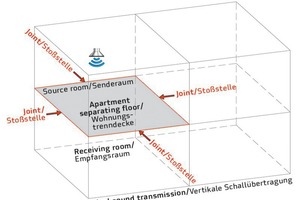
The horizontal impact sound transmission value L’n,w to adjacent rooms is exclusively determined by the floor construction and the apartment separating floors. The requirements of DIN 4109 are always met by concrete floor slabs of all kinds and floating screed applied in the usual screed thickness and impact sound insulation boards of common dynamic stiffnesses. All Brespa floor slabs using an impact sound insulation with a dynamic stiffness of 10 MN/m³ achieve the enhanced requirements according to supplementary sheet 2 of DIN 4109.
The situation of the vertical impact sound transmission value L’n,w is similar to the horizontal impact sound, however, the wall weight of the flanking elements and the suspended ceilings are also of importance. If the weights, already needed to fulfill the other sound transmission values, are applied for the flanking walls, and if the floating screed is designed in the usual screed thickness and impact sound insulation boards of common dynamic stiffnesses, then the calculation results of the sound calculation software show that multi-story residential construction using all kinds of concrete floor slabs always will fulfill the requirements according to DIN 4109. All Brespa floor slabs and impact sound insulation boards with a dynamic stiffness of 10 MN/m³ also achieve the enhanced requirements according to supplementary sheet 2 in this case. Additional suspended ceilings are possible as an alternative.
Summary
When the new DIN 4109 is legally introduced in the end of 2016, this will tighten the requirements in multi-story residential construction only marginally. Good sound insulation is still achieved by heavy building components and multi-layered construction. For walls it is true: High densities or facing layers are favorable. Floor constructions with floating screed, using impact sound insulation boards with as low dynamic stiffness as possible, are particularly effective in terms of sound insulation. It is decisive for story floors that concrete floor slabs are installed, either cast-in-situ floor slabs or precast prestressed concrete hollow core floor slabs.