Important additives for building protection
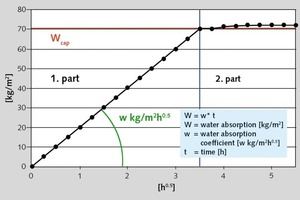
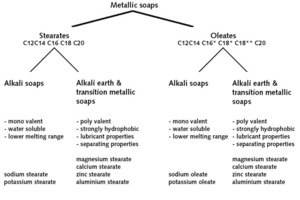
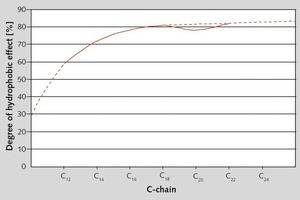
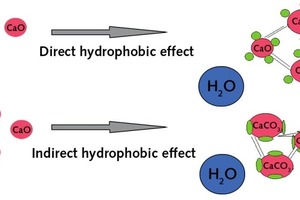
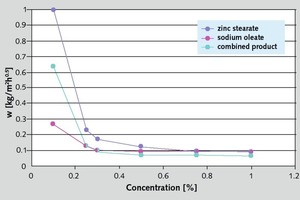
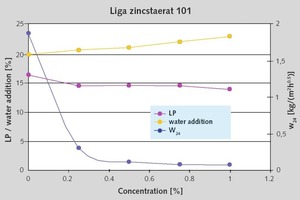
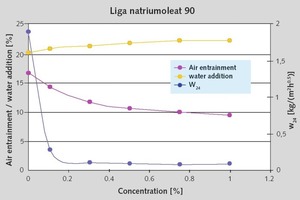
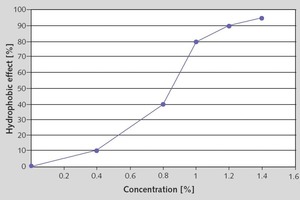
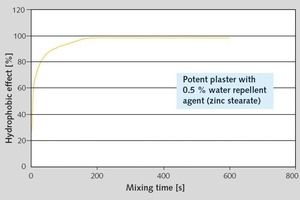
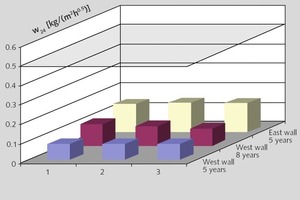
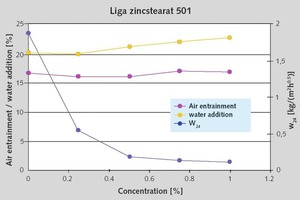
Oleochemical raw materials, namely metallic soaps and sodium oleate are characterized by a beneficial cost/performance ratio. The water absorption coefficient (w) in water resistant plasters has to be below 0.5 kg/m2h0.5. To achieve this, metallic soaps are widely used. An essential criterion in this application is the quality of stearate. Mainly precipitate stearates, with their high specific surface, perform well. While using sodium oleate during the setting of the render, a reaction with calcium ions in the cement or limestone takes place and the oleates are transformed to hydrophobic metallic soaps. The interaction with other raw materials in the plaster formulation is much more pronounced. Product mixtures of stearates and oleates could be an answer to this problem.
A natural decline process occurs in almost all things we perceive in our environment. Wherever possible, human beings try to protect ventures, undertakings against this process. This protection can also be applied to buildings, because they are clearly visible signs of human creativity and they decline when they are subjected to the adverse affects of environment. Water is the most common cause of serious damage. It is responsible for the transport of harmful substances like salts, promotion of the growth of micro-organisms and frost damage in cold periods. Also, heat transition is directly...