New design options through concrete façades made of carbon-reinforced concrete – safe assembly due to approved fastening systems
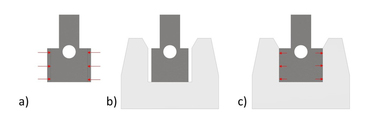
Because of the minimum concrete cover, the previous minimum thickness of façade panels made of steel-reinforced concrete amounts to 7.0 cm, with the façade anchor plates being approved by building authorities for such panel thickness so far. Since there are no requirements for reasons of corrosion protection for non-metallic reinforcement, it is possible to fall below this minimum dimension considerable. The minimum thickness of the components is now resulting from requirements on the load-bearing capacity and from boundary conditions regarding the manufacturing process. A façade panel must feature adequate resistances in order to absorb the design-relevant actions reliably, which are usually actions caused by the wind load and the dead load of the façade panel. While the shear design and the bending design of textile-reinforced concrete panels have been widely investigated and governed, no generally applicable rules can yet be derived for a local verification of fastening points, this means that a verification of a fastening element used in such thin concrete panels by calculation is not possible at present.
In particular, point-by-point fastening systems show great sensitivities in respect of local crack formation. As a consequence, concrete may split or peel-like spalling may occur, with leading to large scattering within the experimental results. When determining a characteristic resistance of a fastening element, this results in substantial reductions of the values if the fastening element is structurally not designed for the specific application in thin façade panels made of carbon-reinforced concrete. National technical approvals provide for planning reliability here. The resistances required for planning of a façade fastening system were determined on the basis of tests and are specified in such an approval.
The fundamental tests as well as the loadbearing effect of point fastening systems will be presented in the lecture and the construction method will be explained with the aid of examples of executed structures.