Precast concrete – a gamechanger in sustainable construction
The built environment creates approximately 40% of CO2 emissions globally, of which 27% comes from building operations and 6% from the building construction industry, according to Architecture 2030. This also means that the construction industry has big opportunities in cutting down emissions, and precast can have a huge impact.
The need for housing, infrastructure, and construction is growing, while carbon emissions need to be cut significantly according to sustainability targets. To make the change, innovations, new technologies, and sustainable raw materials are needed.
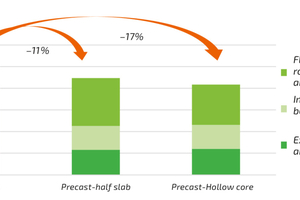
Precast is one existing technology that can significantly contribute to making a difference. The CO2 footprint of a precast building can be even 25% smaller than that of a concrete building created with traditional methods. With precast solutions, it would be possible to reduce the emission based on cement and steel compared to cast-in-situ. In precast, cement use is cut by one-third per m3 of concrete because of the effective compaction process in the factory, and, because steel for precast is prestressed, about 10-15kg less steel per m2 of the floor slab is needed.
Furthermore, precast factories using modern technologies save cement, concrete, and water – and can reduce CO2 emissions. The precast method has a sustainable lifecycle when machinery is maintained, precast slabs and leftover concrete recycled, and CO2 emissions in production systematically decreased.
The challenge is that cost is still the main driver. Adopting new technology costs, and few companies are willing to change technology without compensation.
Developments in precast production technologies
Some very efficient technologies from the point of view of concrete usage have been available for a long time already. For example, shear compaction technology, that Elematic extruder hollow core casting machines use, is at the core of sustainable precast production. This technology minimizes the amount of empty space between aggregates in concrete, which decreases the use of cement. It also enables the use of more crushed stone, which decreases the use of natural resources, and increases precast slab strength, which improves the durability and safety of precast buildings.
As processes are developed and automated in precast factories, material loss in the production process can be further cut down.
For example, during the hollow core production process, automatic concrete recycling can significantly reduce CO2 emissions, concrete waste, and costs. Elematic has introduced this kind of system to the market. In this solution, concrete dug from openings and recesses for HVAC ducts is automatically recycled back to casting, in other words, to slab production.
Furthermore, Elematic has also introduced a carbon footprint evaluation service that calculates and finds ways to decrease the greenhouse gas emissions caused by hollow core production at precast plants. The evaluation takes into account water, cement, other raw materials, energy, waste, and transportation.
On the wall production side, side profiles and shuttering of concrete molds are traditionally made of wood. A reusable system of aluminum profiles and magnet shuttering, such as Elematic FaMe, enables precast plants to cut monthly LVL usage by 50% while it at the same time can save up to 70% of shuttering time.
In addition to machinery and services, precast production digitalization is another factor that helps optimize the use of beds and tables, which, in turn, reduces waste in materials.