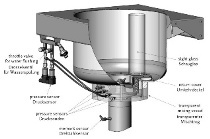
Using power ultrasound to improve cement suspension workability
In the field of concrete technology, the concept of workability describes that property of concrete that determines the ease and homogeneity with which it can be mixed, placed, consolidated and finished (cf. ACI 116R-90). Workability is thus a generic term used to refer to individual „stages“ of the process of producing fresh concrete. Consistency is crucial in this regard because it influences, for instance, mixing times, the degree of pumpability or required compacting work. The results outlined in this article demonstrate that power ultrasound (PUS) is not only an attractive method for accelerating setting and hardening processes but can also positively influence properties relevant to workability.
Acoustic vibration in the range from 20 to 100 kHz is termed ultrasound [1]. The term power ultrasound is used if the energy density of these sound waves exceeds the intensity threshold of 1 W/cm². As a result of this high energy density, items subjected to ultrasound may be destroyed or altered in a targeted fashion [2]. In a fluid, the application of PUS causes cavitation, which is the formation and implosion of voids in fluids due to pressure variations. This phenomenon is considered the most important effect caused by ultrasound [3]. It is assumed that the vigorous implosion of the...