A cover for sandwich wall panels
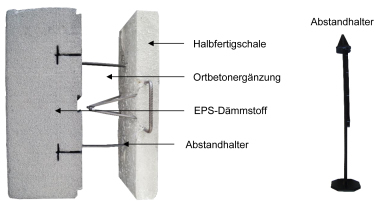
Multi-layer reinforced-concrete wall panels comprise a supporting and facing shell made of reinforced concrete as well as an interior insulating layer. The facing shell, which forms the façade, has a minimum thickness of 70 mm, is generally non-load-bearing and serves as a weather protection layer for the thermal insulation and as a design feature of the building. Despite having a non-load-bearing function, these façades are of solid design because the internal reinforcement must be protected against corrosion. Innovative developments in the fields of concrete engineering and anchoring technology enable slender, non-reinforced, energy-efficient and sustainable architectural concrete façades with a component thickness of merely a few centimeters to be built as the facing shell of multi-layer reinforced-concrete wall panels (Fig.). This potential presents itself through the use of ultra-high performance concretes which are characterized, for example, by their high tensile strength and flexural strength. Connectors made of glass fiber-reinforced polymer material allow multiple and hyperstatic mounting of the façade without the formation of thermal bridges. Stresses resulting from restraint action can be reduced due to the comparatively low modulus of elasticity.
In order to be able to design this system, comprehensive small-scale testing on the material, component testing on the façade system and numerical investigations are performed at TU Kaiserslautern. The investigations focus, for example, on determining structural element resistances taking into account load-bearing direction, scale effect and exposure, and on the influence of the supporting structure on the load-bearing behavior. The results will be incorporated in a design proposal that will be verified by means of component testing. Construction recommendations will be developed for the actual production process at the precast plant. The objective is to enable the use of non-reinforced UHPC in the cover of sandwich wall panels.