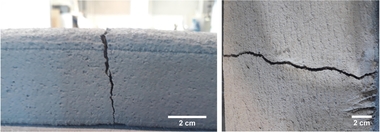
Chemical attack on concrete
Concrete is exposed to external chemical attack in various areas of application. This can seriously impair the durability and performance of a structure. The reactive component of the concrete to chemical attacks is essentially the cement paste. Depending on the type of the aggressive substances, different damage processes result. While acid has a solvent effect, the sulfates penetrating the concrete produce with constituents of the cement paste secondary sulfate phases, e.g. as ettringite, gypsum or thaumasite, that can trigger expansive/destructive processes. Exchange reactions in the cement...