Classification of ultra-high-performance concrete
The DAfStb Guideline on “Ultra-High-Performance Concrete” will significantly expand the range of structural concretes compared to DIN EN 206. Compressive strength and axial post-cracking tensile strength are key strength parameters of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete (UHPFRC). Based on these parameters, UHPFRC is classified into concrete strength classes and performance classes.
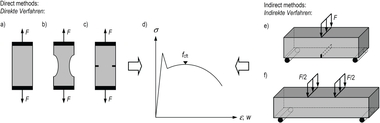
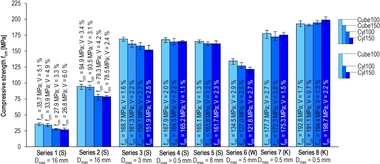
The compressive strength test is carried out in accordance with DIN EN 12390-3, where UHPFRC test specimens of different shapes and sizes show compressive strength ratios deviating from that of normal-strength and high-strength concrete. These ratios also essentially depend on the fiber volume fraction and the fiber orientation relative to the direction of compression. The flatness and parallelism of the loaded surfaces have a greater influence on the results of compressive strength tests on UHPFRC than in the case of normal-strength and high-strength concrete. The highest compressive strengths with low scattering are obtained by grinding even the loaded surfaces of the cubes. Because of the overall higher standard deviation, the compressive strength conformity criteria were adjusted for UHPFRC.
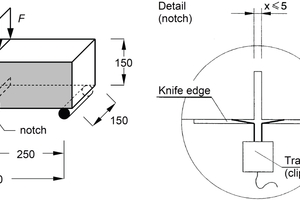
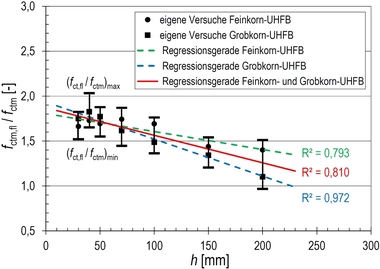
The axial post-cracking tensile strength is defined as the maximum nominal concrete tensile stress under axial tension which can be carried by the action of fibers in the cracked state. It is determined not directly but by means of a bending test. Contrary to the DAfStb Guideline on “Steel-Fiber-Reinforced Concrete”, the bending test is performed in accordance with DIN EN 14651 as a 3-point test on a notched beam. Taking into account the non-linear stress distribution occurring in the cracked state, the basic value of the axial post-cracking tensile strength is derived from the residual flexural tensile strength at a small crack mouth opening displacement. Based on this value, the tested UHPFRC is assigned to a performance class.