Shear design of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete girders
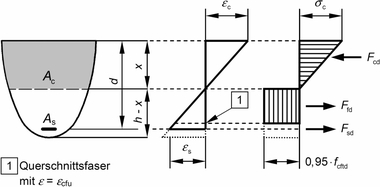
In [1], an approach for verifying the shear resistance of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) girders is presented. This approach follows Eurocode 2 and the German DAfStb Guideline on „Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete“. It superimposes the shear resistance of a member without shear reinforcement, the shear resistance provided by stirrups, and the contribution of the fibers in the shear crack. Regarding the latter, the approach differentiates between members with I-shaped and compact cross-section because crack formation and failure mode differ significantly for the two types of cross-section. Consequently, the efficiency of the fibers in terms of shear resistance is mathematically doubled for members with I-shaped cross-section compared to the current approach described in the DAfStb Guideline on „Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete“. This allows for a more economical design of such members. In contrast, a further reduction of the efficiency of the fibers is required for members with compact cross-section.
In [2], the proposed design approach is validated by means of a shear database. When compiling the database, the compressive strengths and post-cracking tensile strengths from the literature had to be critically reviewed and converted with respect to the specimen size and test method. The model reliability was statistically analyzed for various specimen configurations and model parameters. It was found that shear slenderness and post-cracking tensile strength influence the model safety the most, while the other parameters showed only a minor effect. For 133 tests on beams with I-shaped cross-section, the mean value of the model safety is X̅ = 1.48 and the 5 % quantile is Q0.05 = 0.94. For 75 tests on beams with compact cross-section, the results are X̅ = 1.59 and Q0.05 = 0.94. For all 208 tests included in the database, X̅ = 1.52 and Q0,05 = 0.94 are obtained.

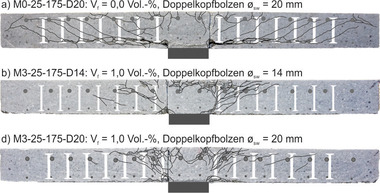
![Fig. 1: Typical crack pattern for a) shear tension failure of a girder with I-shaped cross-section and b) diagonal tension failure of a girder with compact cross-section [1]](https://www.bft-international.com/imgs/2/0/9/0/5/9/6/tok_b35ddf427e744eb528cd184ec17bfbe1/w300_h200_x600_y554_12_8_Metje_Abb_red-7d83de102c681489.jpeg)