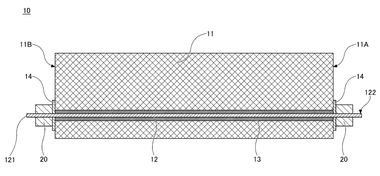
Optical inspection of button heads
on prestressing steel
Button-headed prestressing tendons are used with end-anchorage for wire tendons in railway sleepers and for poles and towers. Button-headed prestressing wires have two advantages over stranded prestressing tendons: there is no loss of pretensioning force due to wedgeslip and there is, in addition to bonding, an end anchorage through which the tensioning force is applied.
The button heads are produced in series, usually on automatic button-heading machines. Process faults that occur during heading can result in geometric irregularities. Cracks can occur during cold working due to fluctuation in material properties. Use of button-head tendons with faulty button heads can cause failure of the tendon. The exchange of prestressing wire in subsequent processes results in downtimes of the machines, reworking, and high material consumption.
Solution approach with automatic image processing
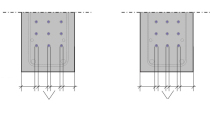
A camera system with advanced image processing stationed directly downstream of the button-heading machine automatically detects geometrical faults and cracking on the button-heads. The system inspects every head within approx. 10 seconds. During this period, it positions and fixes the prestressing steel, and several cameras take two pictures each with different lighting. Following evaluation of the pictures, faultless button-headed tendons are passed on to the subsequent processes, and faulty button heads are automatically cut off, together with 10 cm of wire, and are disposed of.
The image processing works with very high, constant reliability for optimizing the production process and minimizing reject waste, but does not replace safety-relevant inspection. Material consumption and worktime can be notably reduced.