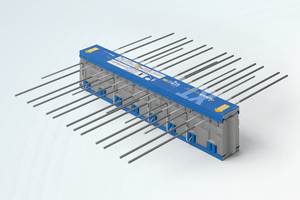
Regulated fire protection in the approval
The model regulation for high-rise buildings requires non-combustible products in façades of high-rise buildings of more than 60-m height. Authoritative for the combustibility of construction products is the fire action released as energy. The structural thermal insulation product Schöck Isokorb is approved for use in non-combustible façades. Conformity has been established in an expert opinion by the MFPA Leipzig Institute for Materials Research and Testing, based on its high fire resistance duration of REI120 and encapsulation with fire-resistant cladding.
A comparison of fire action, in which the fire action was compared with other construction products, confirmed that the fire action of window frames, and/or EPDM sleeves for glass, is many times higher in balconies or exterior corridors fitted with Schöck Isokorb. 100 m² composite thermal insulation systems on high-rise buildings with windows, doors and balconies served as reference façade in the comparison.
Regulated fire protection in the approval
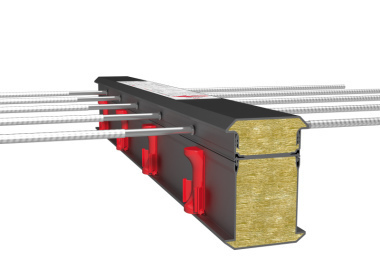
When fire protection is specified for planning and by the building law, Schöck must plan and implement Isokorb with fire-resistant cladding. The fire protection variety satisfies all requirements of the building law and can be used as fire barrier. To achieve a fire resis-tance duration of 120 min., the product was tested several times in an encapsulated room. The fire-resistant cladding ensures that the structural components, for example, shear/tension bars and concrete thrust bearing, are sufficiently protected from fire during the specified duration and that their loadbearing effect is retained (criterion “R”) and the insulation (criterion “I”) is ensured. Lateral swelling tapes or projecting fire-resis-tant cladding elements ensure integrity (criterion “E”) in the event of a gaping joint (cracking). This fire protection enables the use of structural thermal insulation elements from Schöck for escape and rescue routes.
Use in non-combustible façades
All loadbearing components of Schöck Isokorb are made of non-combustible materials. The fire action results essentially from the Neopor of the insulation body. The high-rise model building code specifies in section 3.4 for external walls that specific construction products in external walls, e.g., window profiles, seals etc., are exempt from the non-combustibility rule, i.e. they may be made of normal inflammable materials, such as the insulation bodies from Isokorb, provided the fire action is adhered to. Schöck Isokorb satisfies these constraints.