Thermal anchor: lower U-value dispenses with detailed thermal bridge calculation
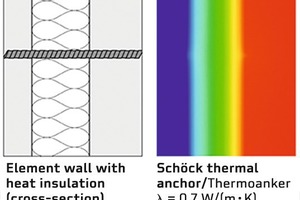
Current calculations show that the Schöck thermal anchor allows design engineers to dispense with complex and detailed thermal bridge calculations as its thermal conductivity is very low at a lambda value of 0.7 W/mK.
The EN ISO 6946 standard governs the method of calculating the thermal resistance (R-value) and thermal transmittance (U-value) of structural components. It specifies for a correction of the U-value to be made in case of point penetrations, which requires an additional calculation to be made by the design engineer. This correction can be dropped, however, if ∆Uf (number of penetrations multiplied by point thermal transmittance) is smaller than 3 %. The current study on conducting three-dimensional thermal bridging calculations for thermal evaluation of Schöck’s thermal anchor types H and D shows that the value for the Schöck thermal anchor in standard design is significantly below the required limit. The use of Schöck thermal anchors thus dispenses with having to perform an additional detailed thermal bridge calculation in the design stage.
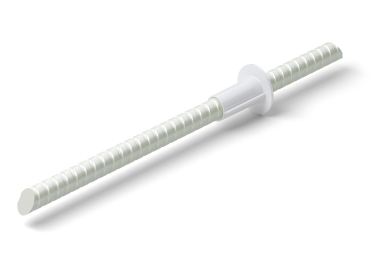
The Schöck thermal anchor is an energy-efficient connector made of glass fiber-reinforced polymer for use with sandwich and element walls. It replaces the conventional lattice girder and optimizes the wall in terms of energy efficiency. In February 2015, the Schöck thermal anchor was certified as a passive house component in the façade anchor category. The Passive House Institute tests and certifies products with regard to their suitability for use in passive houses. The use of certified products helps design engineers to ensure proper functioning of the passive house.