ReBuild – reutilization of entire reinforced-concrete
elements
The high demand for construction materials, together with large overall quantities and limited availability, have an increasingly adverse impact on eco-systems and lead to loss of land. Reinforced-concrete construction, as the most widespread building method using cement in its constituent materials, in addition to steel, significantly contributes to this situation. Cement production alone gives rise to 8 % of greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. The increasing use of recycled concrete is welcomed, but cannot alone solve these challenges.
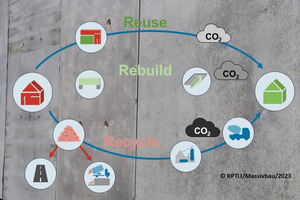
Essential, in addition, are circular material cycles and reutilization on the same level instead of down-cycling. With this objective in sight, the RPTU- project ReBuild focusses on reutilization of entire reinforced-concrete construction elements in the sense of urban mining.
One of the important research topics is development and practical implementation of reversible inclusion of building components. Here, elements of floor slabs, walls and columns especially offer considerable
potential for reutilization. However, to ensure these benefits, new process chains are essential prerequisites.
In future, with the aid of digital stocktaking systems, inventory structures can be quickly and precisely analyzed and processed in preparation for subsequent work processes. Here, digital twin building,
in addition to detailed reporting on the current status, also enables phased planning for selective dismantling, as well as subsequent reutilization. Various areas of application are basically conceivable: e.g., reutilization of an existing floor system for a new floor, or also as alternative product – for example as L-wall. In this way, adherence to the climate protection goals in the construction sector must in future go hand in hand with the development of new business models for building contractors, precasters, demolition companies and other industry stakeholders.