Recycling of lightweight concrete as a central modul for circular, CO2-absorbing concrete systems
New strategies are needed to make the construction sector more sustainable while meeting increasingly demanding environmental requirements. At the Institute of Construction Materials at the University of the Bundeswehr, a research program is currently underway to mitigate environmental impact by closing material cycles and exploiting the potential for CO2 sequestration in recycled materials to optimize concrete towards the net-zero target.
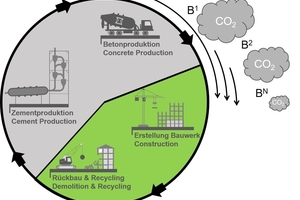
This project addresses the limited recycling options for lightweight concrete, which is currently excluded from standardization. It was shown that lightweight concrete components at the end of their life cycle (B1) can be converted into renewable recycled aggregates through appropriate processing. The mechanical, thermal, and CO2 absorption characteristics of the recycled materials are assessed to verify their suitability for new concrete mix designs and to quantify their CO2recovery potential for LCA purposes. Based on this characterization, recycled materials will be used to produce a new generation of lightweight concretes (B2) in which the original lightweight aggregate is substituted completely while replicating the properties of the original lightweight concrete. Characteristic concrete technology parameters such as compressive strength, modulus of elasticity, and thermal conductivity are assessed to ensure that these recycled-aggregate concrete mixes meet structural design requirements.
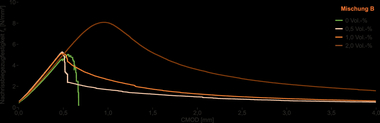
To validate the long-term potential of this approach, the recycled concrete (B2) will also be processed, and the properties of the resulting recycled materials (BN) will be reassessed. The focus of this research is on quantifying the CO2 uptake of the recycled materials, their share in the total capacity, and their relation to global warming potential over several life cycles. This project investigates aspects of recycling various types of lightweight concrete, including crushing, processing, and screening techniques to produce recycled aggregates.