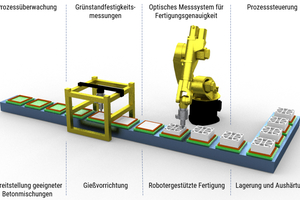
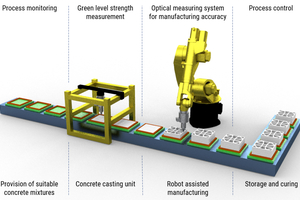
Efficient production of precast elements suitable for lightweight construction by combining additive concrete extrusion with conventional production processes
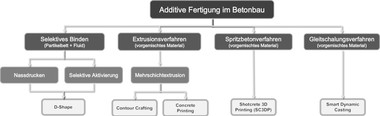
Additive production processes provide ample design freedom in combination with utmost precision and a high degree of automation, which is why they may potentially become the key technology in the construction industry. However, the layered surface structuring of the resulting precast elements inherent in the process often stands in the way of a more widespread application, particularly if the concrete extrusion method is used. Combining additive concrete extrusion with conventional production processes such as concrete casting and shotcreting makes it possible to fully utilize the advantages of each of the technologies for implementing the efficient production of precast elements suitable for lightweight construction while conforming to a high surface quality standard.
Basic research projects currently underway at TU Chemnitz investigate two new additive methods combining shotcreting with extrusion and casting with extrusion, respectively, in terms of material and technology requirements while identifying potential areas of application by producing a select range of demonstrators.
The shotcreting/extrusion method is particularly well suited to producing wall and façade panels. It combines a thin shotcrete layer and an extruded reinforcing structure with integrated load application elements to manufacture exceedingly efficient structural components that provide the specified load-bearing capacities and high-quality surfaces. The newly developed combined shotcreting/extrusion nozzle makes it possible to both spray and extrude mortars and concretes adjusted to the specific project requirements.
The casting/extrusion method opens up enormous potential for formwork-free construction techniques, for instance in the manufacture of precast stairs. For this purpose, the form is first extruded to act as permanent shuttering, followed by integration of the required reinforcing and fastening elements, and the final casting step. In the production process, formwork edges and surfaces need to be accurately defined and aligned in order to ensure the specified bond characteristics and surface qualities.
Weitere Autoren / Further Co-authors:
Dipl.-Ing. (FH) Ralf Gliniorz, Dipl.-Ing. Henrik L. Funke