Industrialization of precast concrete construction –
Priority Program 2187
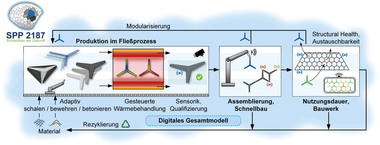
Building fast and in a resource-efficient manner is a challenge of our times. It is imperative to minimize disruptions in infrastructure and CO2 emissions because of construction activities. In the context of the Priority Program 2187 “Adaptive modularized
construction made in a flux – precise and rapid building of the future” funded by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG), approx. 60 researchers have been working on solutions for this purpose since 2020 [1]. Therefore, individual load-bearing structures are divided into modules, industrially prefabricated, and just have to be assembled on site following the Lego principle. The prefabrication of the modules takes place in a quality-assured manner, using lean production methods.
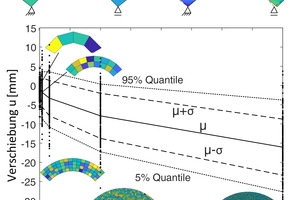
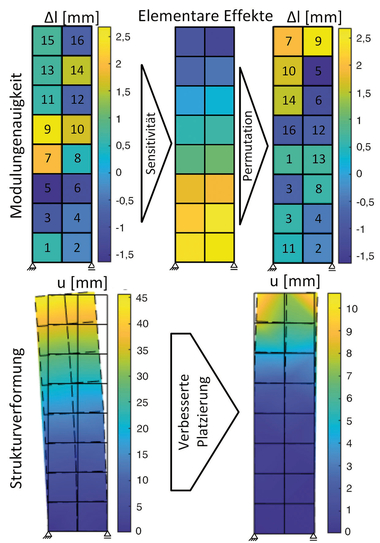
The segmentation of the load-bearing structures into modules leads to the fact that inaccuracies can superimpose each other, such as deviations in the geometry of the individual modules, overlapping in favor of the overall load-bearing structure. This effect is intensified
by the number of modules being used for a structure. The figure
illustrates this, using the example of an arched structure, by means of a stochastic evaluation of the deviations in mean value and standard deviation subject to the number of modules. The modules tend to be assumed too small. As countereffect, a high accuracy of the modules is required or a compensation of the deviations by a purposeful
arrangement of the modules (“too short compensates too long”).
Current developments in the context of the SPP are first implementations of prototypes consisting of automatically manufactured similar modules as well as interdisciplinary benchmarks. The latter include feasibility studies of the modular segmentation for bridge support structures, in which different module and joining concepts are combined so as to result in the bridge design; integrated planning in building constructions, being derived from a holistic digital representation of a specific modular building construction project; as well as process-related quality assurance close to real time and with large-scale tomography, by investigating the quality control of the internal structure and external shape of modules as an in-line process.