Thermally optimized façade design for precast elements
Increasingly demanding energy efficiency specifications for new buildings or extensive refurbishment projects require not only appropriate building services and installations that consume the least possible amount of energy but also a thermally optimized envelope. To meet the requirements of the applicable Energy Saving Regulation, it will no longer be sufficient to apply the previous approach of considering heat losses through planar structural components, combined with a general allowance for heat losses in weak spots resulting from the particular shape or material used for the relevant element(s).
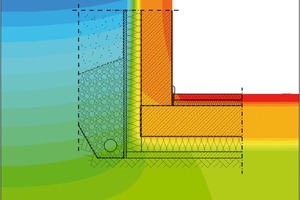
This is why the detailed design and verification of such connecting areas is crucial to ensure a high quality standard of the envelope of highly insulated buildings.
In response to this situation, the Chair of Structural Physics and Building Services at TU Dortmund has been cooperating with the German cement and concrete industries in the past few years to publish the Design Atlas for Building Construction (Planungsatlas Hochbau). This comprehensive database includes connection details of various façade systems for residential and non-residential buildings. The associated range of data comprises verification of heat losses through the relevant connection, as well as heat losses through the adjoining standard component and the minimum surface temperature. Users can vary these parameters by selecting different thicknesses and insulation quality standards in order to thermally optimize the relevant connection design or to compare the selected design with alternative solutions. Compared to the previously applied general allowances, this method enables consideration of a significantly lower allowance for thermal bridges across the entire building envelope.