Fatigue resistance of dry joints under compressive loading in modular concrete structures
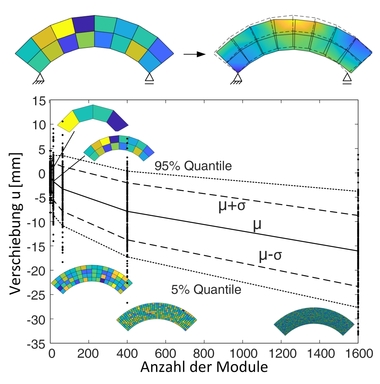
In modular structures, prefabricated concrete modules are usually joined via dry joints to form a supporting structure. This construction method enables serial, resource-efficient and quality-assured prefabrication of the modules as well as simple and rapid assembly and disassembly on site. It is particularly suitable for the construction of large-span segmental girders and modular shell structures and is already being used for erecting concrete towers for wind turbines and segmental bridges. These structures are subject to high dynamic loads, whereby current regulations do not contain any approaches for the verification of concrete dry joints under cyclic compressive loading and drafts of new standards assume high reductions in joint load-bearing capacity depending on the joint surface characteristics. For this reason, contractors currently provide a very high fitting accuracy, which is ensured by grinding for smooth joints and by the match cast method for keyed joints.
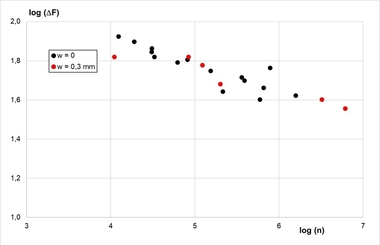
To investigate the fatigue behavior of concrete dry joints, two-part test specimens with ground, sawn, and milled joint surfaces were manufactured. Their surface roughness was analyzed using a tactile profilometer, and their fitting accuracy was analyzed using 3D scanning. Subsequently, their load-bearing capacity was tested. Under monotonically increasing compressive loading, ground dry joints achieved load-bearing capacities and failure mechanisms comparable to monolithic test specimens. Under cyclic compressive loading, the fatigue strength of the two-part test specimens was generally lower than those of monolithic test specimens and exhibit greater scatter, particularly for sawn and milled joint surfaces. The results provide crucial insights into the fatigue resistance of concrete dry joints under compressive loading, which are essential for the widespread use of fast and resource-efficient modular concrete construction.